
The array is sorted when all the unsorted elements are placed at their correct positions. In each iteration, the comparison takes place up to the last unsorted element. CLR-1 : Utilize the different data types Utilize searching and sorting. The same process goes on for the remaining iterations.Īfter each iteration, the largest element among the unsorted elements is placed at the end. The above process goes on until the last element.Now, compare the second and the third elements.I find it more intuitive to loop from 1, so like the code below. For each element look at all remaining elements on one side and swap them if necessary. method was implemented in an algorithm written in the Scilab (2006) language. If the first element is greater than the second element, they are swapped. The point of bubble sort is to loop through all elements. The list of clusters and genes is further sorted based on the information.Starting from the first index, compare the first and the second elements.Suppose we are trying to sort the elements in ascending order. Just like the movement of air bubbles in the water that rise up to the surface, each element of the array move to the end in each iteration.
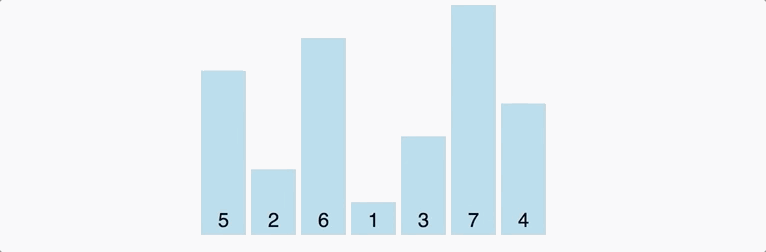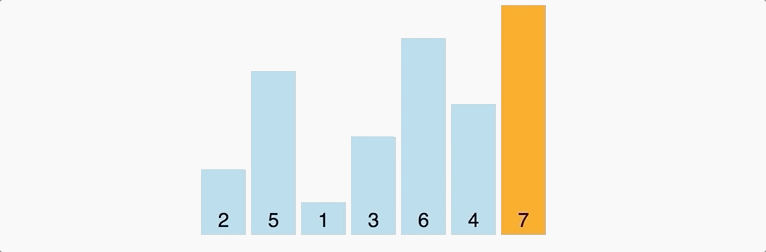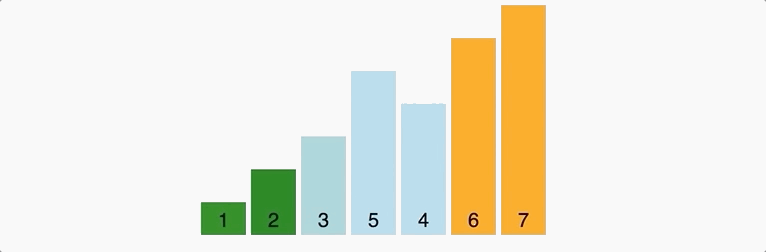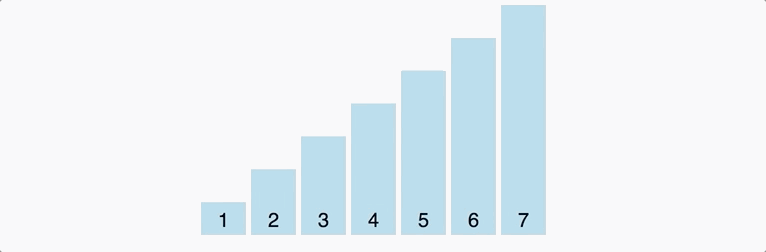 Decrease Key and Delete Node Operations on a Fibonacci Heapīubble sort is a sorting algorithm that compares two adjacent elements and swaps them until they are in the intended order. This continues until for n iterations where n = number of elements in the array. These passes through the list are repeated until no swaps had to be performed during a pass, meaning that the. This is nothing but a recursive argument on the remaining array. Bubble sort, sometimes referred to as sinking sort, is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the input list element by element, comparing the current element with the one after it, swapping their values if needed. By the above recursive argument, this second largest array will then reach the last position in the remaining array (). This algorithm does the swapping of elements to get the final output in the desired order. Here, the largest element in the rest of the array (which is 4) will be nothing but the second largest element in the array. The basic bubble sort algorithm can be explained as follows: bubbleSort (array) for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1. Now that the largest element has reached its correct position (for instance, 5 reached the last position), we can simply ignore it and concentrate on the rest of the array ( in the above case). So, at the end of the first pass, the largest element will always reach its correct position. Introduction to programming in MATLAB/SCILAB : Introduction, M-File Scripts. This is because this largest element will always break the desired order. Student will able to write an algorithm Selection Sort, Bubble Sort. In the first “pass” through the array, the largest element will always get swapped until it is placed to the extreme right. This exactly is how bubble sort in C works.Īs an example, check this graphic that pictorially depicts how bubble sort works. Before we get into the details of the sorting algorithm, let us understand the problem statement. This generally means that we want the data to be sorted in ascending order. The above pseudo-code for Bubble sort algorithm in C takes in an array as an argument and then returns sorted array at the end. Given a data that is sorted in ascending order, reverse it and you will get the data in descending order.ĭue to the similar nature of the 2 orders, we often drop the actual order and we say - we want to sort the data. As we know, Bubble sort in C works by comparing and swapping adjacent elements in an array. Descending order: descending order is the exact opposite of ascending order.
Decrease Key and Delete Node Operations on a Fibonacci Heapīubble sort is a sorting algorithm that compares two adjacent elements and swaps them until they are in the intended order. This continues until for n iterations where n = number of elements in the array. These passes through the list are repeated until no swaps had to be performed during a pass, meaning that the. This is nothing but a recursive argument on the remaining array. Bubble sort, sometimes referred to as sinking sort, is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the input list element by element, comparing the current element with the one after it, swapping their values if needed. By the above recursive argument, this second largest array will then reach the last position in the remaining array (). This algorithm does the swapping of elements to get the final output in the desired order. Here, the largest element in the rest of the array (which is 4) will be nothing but the second largest element in the array. The basic bubble sort algorithm can be explained as follows: bubbleSort (array) for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1. Now that the largest element has reached its correct position (for instance, 5 reached the last position), we can simply ignore it and concentrate on the rest of the array ( in the above case). So, at the end of the first pass, the largest element will always reach its correct position. Introduction to programming in MATLAB/SCILAB : Introduction, M-File Scripts. This is because this largest element will always break the desired order. Student will able to write an algorithm Selection Sort, Bubble Sort. In the first “pass” through the array, the largest element will always get swapped until it is placed to the extreme right. This exactly is how bubble sort in C works.Īs an example, check this graphic that pictorially depicts how bubble sort works. Before we get into the details of the sorting algorithm, let us understand the problem statement. This generally means that we want the data to be sorted in ascending order. The above pseudo-code for Bubble sort algorithm in C takes in an array as an argument and then returns sorted array at the end. Given a data that is sorted in ascending order, reverse it and you will get the data in descending order.ĭue to the similar nature of the 2 orders, we often drop the actual order and we say - we want to sort the data. As we know, Bubble sort in C works by comparing and swapping adjacent elements in an array. Descending order: descending order is the exact opposite of ascending order. 
Here, the “smaller than” relation is actually the “<” operator.
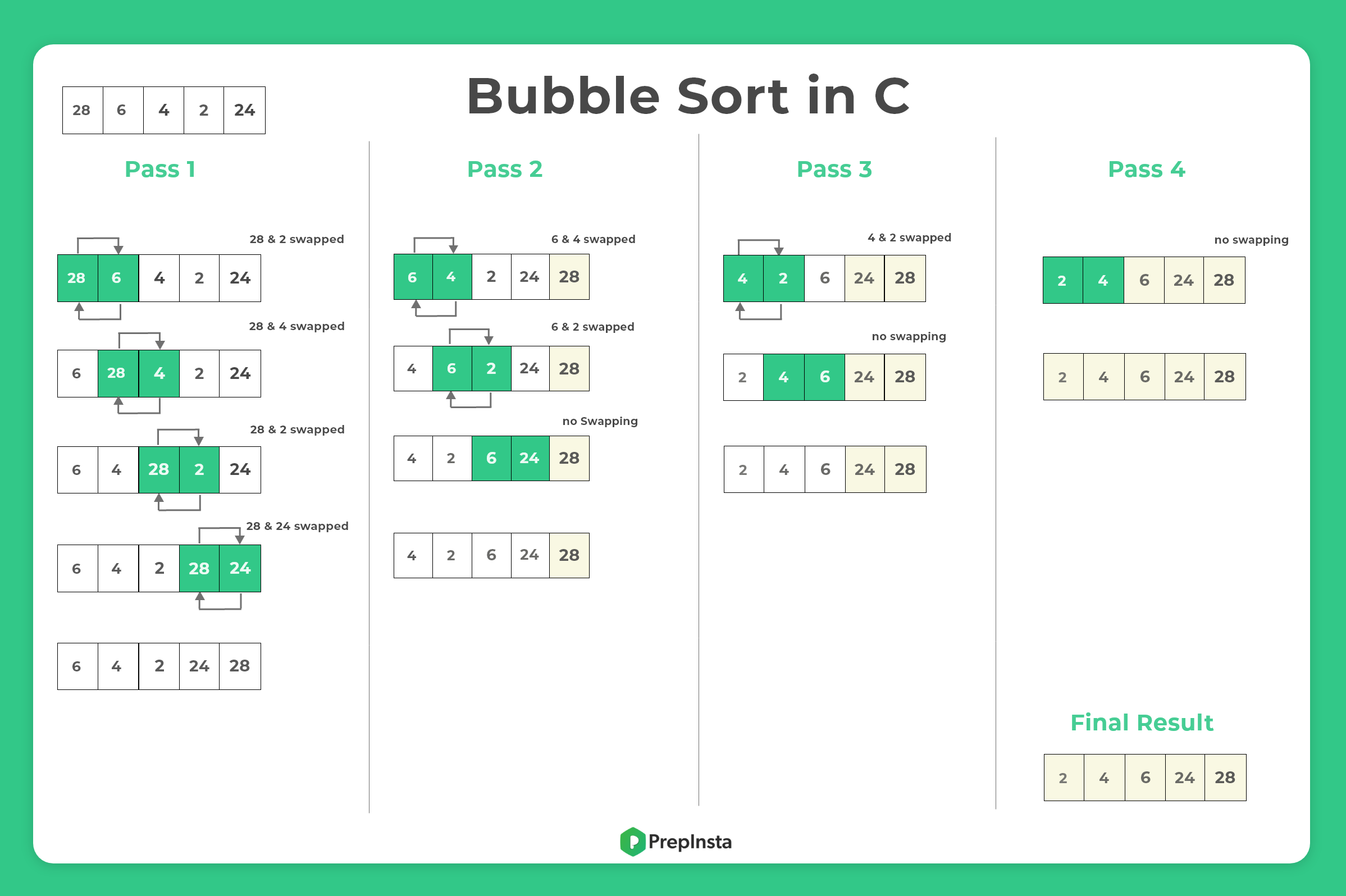
As a simple example, the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 are sorted in ascending order. Soft Computing: With Matlab Programming, N. This “smaller than” relation is an ordered relation over the set from which the data is taken. Internal sorting- Bubble sort, selection sort, insertion sort, quick sort, merge. Ascending order: while sorting the data in ascending order, we try to arrange the data in a way such that each element is in some way “smaller than” its successor.The arrangement of data in a particular order is called as sorting of the data by that order. finding "Joe" in an attendance register of 100 students. These data arrangements give easier access to data for future use for ex. Another example is the attendance register at school/college which contains our names arranged in alphabetical order. For instance, during our school days, we are told to stand in the queue based on our heights. Often in real life, we are supposed to arrange data in a particular order. Sorting forms a great case study for those who want to learn Data Structures and Algorithms. Sorting of data is one of the most fundamental, yet important problem in computer science. Bubble Sort Algorithm in C - Introduction.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
